Professional graphite material supplier, graphite for EV, grease, furnace and any other industries.
(Differences Between Diamond and Graphite: Structure and Properties)
Title: The Unveiling of the Mysteries: Differences between Diamond and Graphite
(Differences Between Diamond and Graphite: Structure and Properties)
Introduction:
As we delve into the world of chemistry and materials science, it is fascinating to uncover the similarities and differences between two seemingly identical substances: diamond and graphite. These fascinating elements have been used for centuries in various applications, but their unique properties and structures have yet to be fully understood. In this blog post, we will explore some intriguing aspects of these two remarkable materials, providing insights into their structure and properties.
Body:
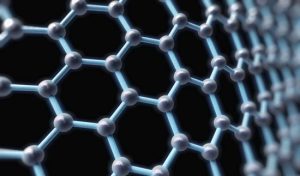
1. Structure:
Diamond, also known as the “best diamond ever made,” has a unique crystal structure that consists of a honeycomb-like arrangement of carbon atoms arranged in alternating layers. The layers can be thought of as honeycombs interlacing themselves like a lattice, with each atom bonding to three other atoms in one plane. This exceptional crystal structure gives diamond its exceptional strength, clarity, and hardness.
Graphite, on the other hand, is composed of(C)。,。。
2. Properties:
Despite having different structures, both diamonds and graphites exhibit some remarkable properties. One of the most significant differences is their optical properties. Graphite is transparent and appears to shimmer in the light. However, diamond exhibits an intense brilliance and shine due to the presence of specific chemical bonds that give it its unique color and transparency.
Another crucial property difference lies in their electrical conductivity. Graphite has low electrical conductivity compared to diamond, making it useful in various electronic applications such as capacitors and transformers. Conversely, diamonds have high electrical conductivity, making them ideal for use in applications requiring high speed data transmission or resistance-to-corrosion testing.
3. Applications:
In addition to their extraordinary physical and optical properties, diamonds and graphites have diverse applications across various industries. In jewelry, diamonds are highly valued for their durability and beauty. In electronics, diamonds serve as reliable conductors for high-speed data transmission and insulation in electronic circuits. In energy storage, diamonds play a critical role in renewable energy applications, such as solar cells and batteries.
4. Future Potential:
With ongoing research and technological advancements, the understanding of these two remarkable materials continues to evolve. As scientists continue to explore new synthesis methods and materials engineering techniques, we may unlock even more hidden properties and benefits from these two extraordinary materials. Whether in the fields of cryptography, medical devices, or environmental sustainability, diamonds and graphites hold great promise for future innovations.
Conclusion:
(Differences Between Diamond and Graphite: Structure and Properties)
In conclusion, while there are many similarities between diamonds and graphites, their distinct structures and properties make them invaluable resources in numerous applications. With continued exploration and research, we can expect further developments in our understanding of these fascinating materials and their potential applications in the years to come.Inquiry us if you want to want to know more, please feel free to contact us. (nanotrun@yahoo.com) hot tags: graphite,graphite powder,nano graphite
(Differences Between Diamond and Graphite: Structure and Properties)