Professional graphite material supplier, graphite for EV, grease, furnace and any other industries.
(how do you think the bonds between carbon atoms might be different in diamond and graphite?)
The bonds between carbon atoms in carbon-based compounds can be quite unique compared to those found in other materials, such as diamond or graphite. One aspect that sets diamonds apart from these other materials is their incredibly strong covalent bonds.
(how do you think the bonds between carbon atoms might be different in diamond and graphite?)
Carbon atoms in diamonds are arranged in a repeating pattern known as the hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure. The arrangement of carbon atoms results in a highly stable, dense, and metallic-like material. This structure makes diamonds highly resistant to wear and tear, making them ideal for use in jewelry, scientific instruments, and other applications where durability is important.
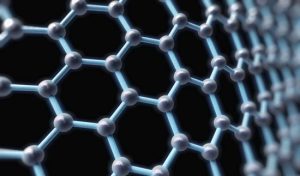
On the other hand, carbon atoms in graphite form more flexible, porous structures known as the amorphous lattice structure. Graphite has a high degree of thermal stability and is widely used in a variety of applications, including electronics, transportation, and construction.
One reason why carbon atoms in diamonds have such strong covalent bonds is that they have a lower energy gap than those in graphite. This means that electrons in carbon atoms are more likely to become excited and lose energy during chemical reactions, resulting in stronger bonds between the carbon atoms.
Another factor that contributes to the strong covalent bonds between carbon atoms in diamonds is the fact that they have a relatively large number of valence electrons compared to other materials. This allows for more electrons to participate in chemical reactions, which can result in stronger bonds and higher levels of stability.
(how do you think the bonds between carbon atoms might be different in diamond and graphite?)
In conclusion, the bonds between carbon atoms in diamonds and graphite are quite different. While both materials have strong covalent bonds, the unique arrangement of carbon atoms in diamonds results in a highly stable and metallic-like material with improved durability. Graphite, on the other hand, has a more flexible and porous structure with better thermal stability, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Understanding these differences can help researchers develop new materials with improved properties and functionality. hot tags: graphite,graphite powder,nano graphite
(how do you think the bonds between carbon atoms might be different in diamond and graphite?)